GreenLetter IX : Power Sector and DSM

Dear Reader,
Do you know that India is the third-largest producer and consumer of electricity globally? It has an installed power capacity of 442.85 GW as of April 30, 2024. The power sector is a key contributor to a country's economic growth. With electricity demand expected to rise by over 60% by 2040, and renewable energy sources expanding rapidly, understanding these trends is more important than ever.

In the 2024-25 Union Budget, the Ministry of Power received an allocation of Rs 20,502 crore—a 16% increase from the previous year. Furthermore, funding for government power sector initiatives has increased by 50%, highlighting a significant push towards enhancing energy infrastructure and sustainability.

Power Sector Landscape
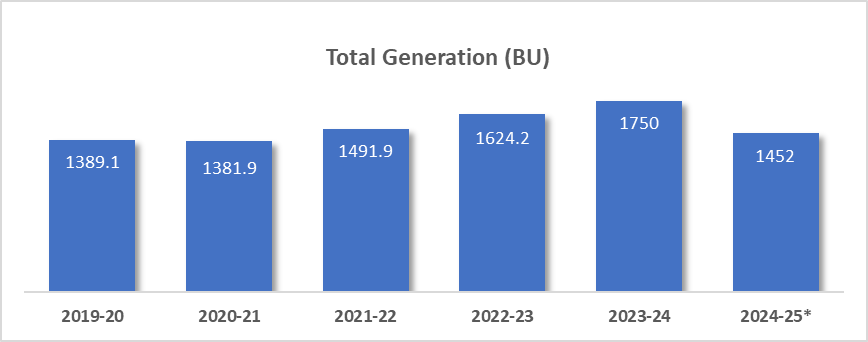
India's power sector is undergoing significant growth and transformation, with a focus on renewable energy and policy initiatives to enhance electrification and meet increasing power demands.
Stages in the Power Sector
India's power sector includes the multifaceted domain from generation to transmission, distribution, and consumption.
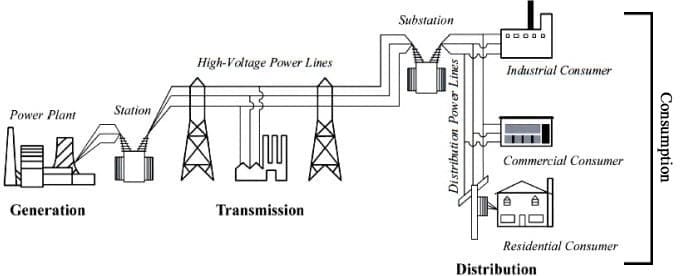
i. Generation: Electricity generation is the first stage in the power sector. India's total electricity generation in 2023–2024 is about 1,750 BU, which is a 7.2% increase from the previous year. The country has also seen an 80% increase in power generation capacity since 2014, reaching 446,190 MW in June 2024.
The generation mix includes:
- Coal and Gas: Approximately 55% of the total capacity, making it the largest source, and the natural gas capacity 10%.
- Renewables: About 30% of the capacity, with significant contributions from solar (15%), wind (12%), and hydro (3%).
- Nuclear: The remaining capacity is split between nuclear (2.5%).
ii. Transmission stage involves the flow of generated electricity from power plants to substations via transmission lines. India's transmission network has increased by 224% since 2014 and extended over 400,000 km. with inter-regional capacity now at 1,16,540 MW.
iii. Distribution utilities supply electricity from the substations to individual consumers through a distribution network that spans over 1.5 million km in India.
iv. Consumption is the final stage where electricity is used by end-users. It involves Residential, Commercial, and Industrial.
Understand the energy losses and challenges at each stage and learn about the efforts to enhance energy security and economic growth.
Who is responsible for What?
To ensure an efficient power sector framework, responsibilities are distributed across various levels, including the Central Government, State Governments, and Private Players. This interlinked structure is essential for managing the entire lifecycle of electricity—from Generation to Transmission to Distribution and Consumption.
Developments in the Power Sector
The power sector is developing with every consecutive year, marking substantial progress towards a more sustainable and reliable energy future. It has seen many developments, including:
- Increased power generation: India's power generation capacity has increased by 194.4 GW in the last nine years.
- Renewable energy targets: India has promised to source half of its installed electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- Increased power availability: The power availability in rural areas has increased from 12 hours in 2015 to 20.6 hours, and in urban areas, it has increased to 23.8 hours.
Have you explored the Power Sector?
India's power sector journey, from advancements in generation capacity to challenges in distribution efficiency. Find our detailed analysis of the power sector in our report.
Read the Article
Power Sector - Demand, Generation & Supply (Part I)Transitioning of Energy and Programs:
As the power sector in India continues to progress, the focus is shifting from simply meeting demand to transforming the energy mix itself. To achieve the goal of 500 GW by 2030, the Indian government aims to add 50 GW of renewable energy capacity over the next five years. As of July 31, 2024, India's installed renewable energy capacity stands at 197.20 GW.
With the increasing integration of renewable energy sources, the role of Demand Side Management (DSM) becomes important in balancing the grid and ensuring efficient energy use. DSM is emerging as a strategy in this transition, offering various programs and initiatives aimed at optimizing energy consumption, enhancing grid reliability, and reducing overall energy costs. Key DSM programs include:
- Standards & Labelling Appliances
- Energy Conservation Building Codes
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
- Agri DSM
- Demand Response
These DSM programs play an important role in supporting India's energy transition. However, despite these advancements, the power sector still faces significant issues that need to be addressed.
Integration of DSM in Energy Landscape
To get insights into the developments of the Power Sector with the shift towards Renewable Energy sources and Energy Efficiency
Read the Article
DSM's Integration in India's Energy Landscape (Part II)Issues in the Power Sector
India's power sector faces significant challenges despite substantial growth in generation capacity, with ongoing issues in transmission and distribution:
- Generation: Installed capacity has increased from 305.15 GW in 2015-16 to 434.2 GW in 2023-24, but grid reliability issues persist.
- Transmission: Transmission lines span 487,587 circuit km as of July 2024, yet modernization is required to reduce energy losses.
- Distribution: Financial losses decreased, but outdated infrastructure and power theft persists.
Issues impacting the Power sector economy:
The power sector in India faces several significant issues that affect the broader economy:
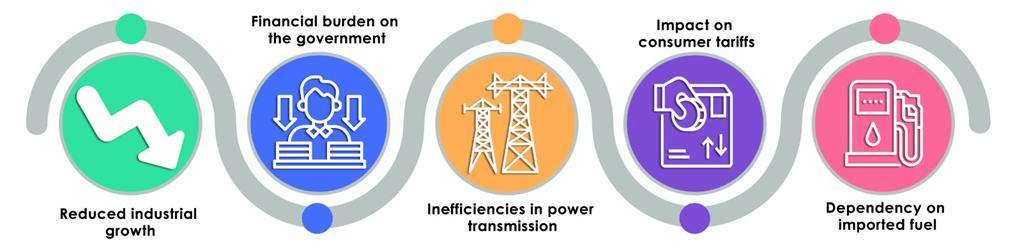
Addressing these issues is crucial for the sustainable development of the power sector and for maintaining economic stability in India. From impacting industrial growth to imposing financial burdens, these issues significantly influence the stability and growth of the economy.
Issues in the Power Sector
To find the reason behind the issues faced by Power Sector in India despite substantial growth in generation capacity
Read the Article
Why India's Energy Future Hangs in the Balance? (Part III)Projects at GreenTree Global
At GreenTree Global, we are committed to driving innovation and sustainability in India’s power sector. Our ongoing projects focus on implementing Demand Side Management (DSM) measures, Energy Efficiency Programs, and promoting the adoption of Renewable energy sources. From enhancing DISCOM capacities to introducing powerful technologies like Energy Efficient Appliances and Agri-DSM solutions, we aim to create an energy-efficient ecosystem that supports India’s transition to a cleaner and greener future.
By working closely with regulatory bodies BEE, SDAs, DISCOMs, ERCs, and industry experts, we continue to outline the energy landscape, ensuring that the ongoing projects not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions and building a resilient energy infrastructure.

News Updates:






Follow our activities on Twitter | Linkedin | Youtube | Instagram | Facebook






