Affordable Cooling through Ceiling Fans in India
Ceiling Fans are playing significant role in enhancing energy efficiency across India's evolving landscape. Discover how super-efficient fans are reshaping energy consumption in the building sector.
By: Dr. Sandeep Garg, Ashish Jindal, Anurag Bajpai, Arvind Tariyal, Syed Faraz, Shikha Saxena
Energy Scenario
Over the past decade, India's energy consumption has doubled to 1624.5 BU, with the building sector accounting for 30%, following the industrial sector.
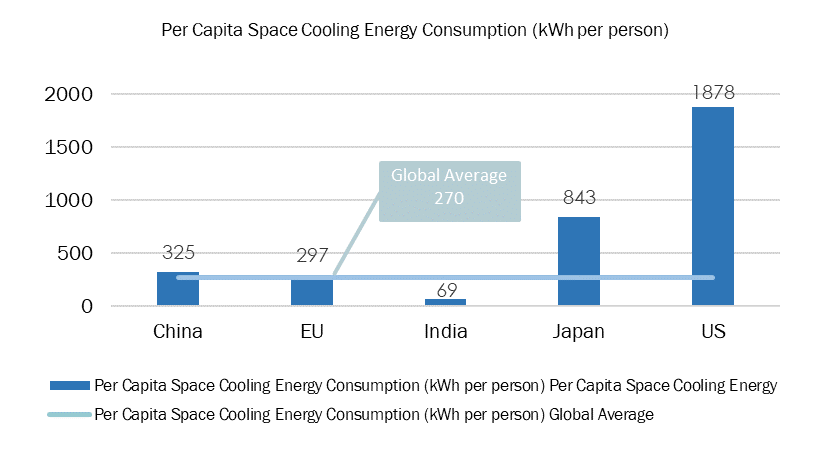
The International Energy Agency's India Energy Outlook 2021 predicts a threefold rise in residential energy use by 2040, driven by increased appliance ownership and a rising demand for cooling. India's per capita energy use for space cooling is currently at 69 kWh, notably lower than the global average of 272 kWh (Figure 1).
Source: India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) report
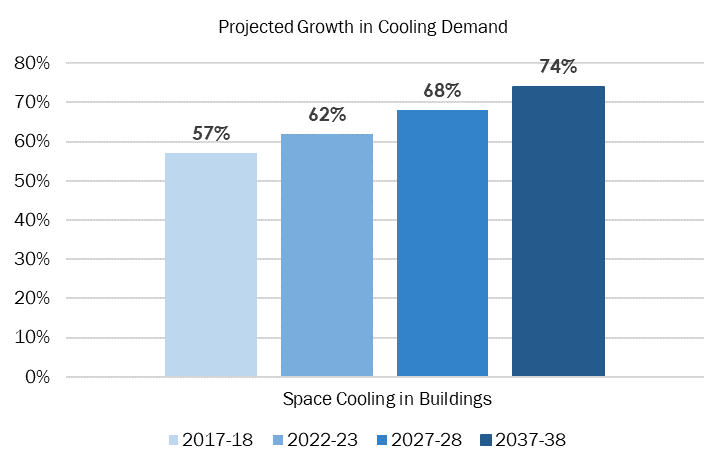
The building sector currently refers 62% as space cooling which is projected to rise to 74% by 2037-38 (Figure 2).
Source: India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) report
The India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) aims to reduce cooling energy needs by 25% to 40% and overall cooling demand by 20% to 25% by FY 2037- 38. Ceiling fans, accounting for 30% of India's cooling energy in 2017-18, are vital. Their adoption of super-efficient fans could decrease usage to 11% by FY 2037-38.
Transformative Changes in Ceiling Fan Energy and Ratings
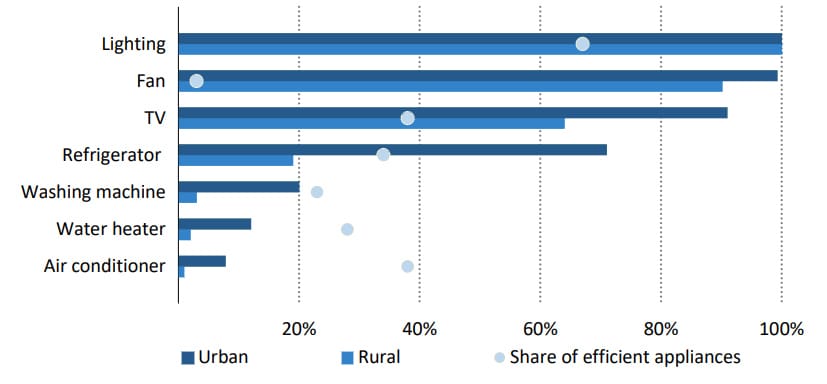
As of 2019, India successfully achieved nearly universal household access to electricity, impacting over 900 million citizens since 2000. Among the primary electrical devices prevalent in Indian households—ceiling fans, LED bulbs, and televisions—ceiling fans hold a ubiquitous presence in both urban and rural areas (Figure 3).
Source: India Energy Outlook 21
The government's impactful Standards and Labeling program significantly contributed to the promotion of efficient appliances. By the year 2020, a substantial segment of ceiling fans and various other devices had attained commendable energy efficiency ratings, as illustrated in (Figure 4).
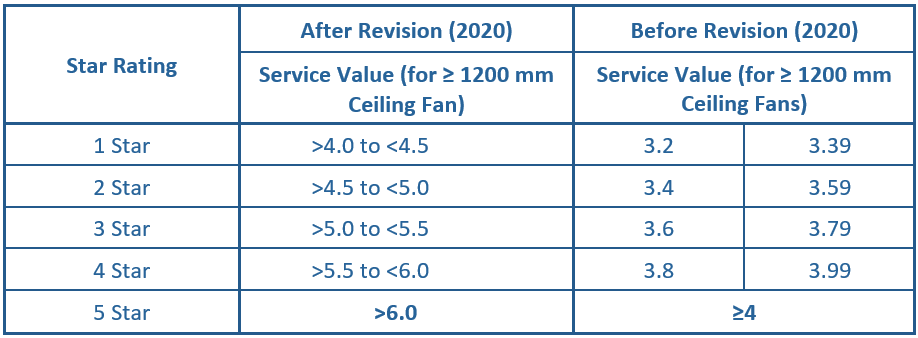
Source: Bureau of Energy Efficiency
Ceiling fans were voluntary in efficiency standards since 2010, becoming mandatory only last year, marking a 12-year span. A pivotal change in 2019 revised ratings from 5-star to 1-star, rendering older ratings obsolete. This led to a significant decrease in the least efficient fans' consumption to around 50 watts from the previous 65-70 watts. Notably, standards had only one revision in 2019 since 2010.
Evolving Trends in Ceiling Fan Energy Efficiency
The latest BEE Impact Assessment (Figure 5) for 2021-22 highlights significant changes in the ceiling fan market dynamics. In 2017-18, 65.86% of Star-labeled fans achieved a prestigious 5-star rating, reflecting a trend towards super energy efficiency (≤35W power for optimal air circulation). In 2020-21, revisions reclassified older 5-star fans as new 1-star models, causing disruption. However, by 2021-22, there was a notable resurgence in Super-Efficient fan sales, demonstrating a clear shift towards higher energy efficiency.
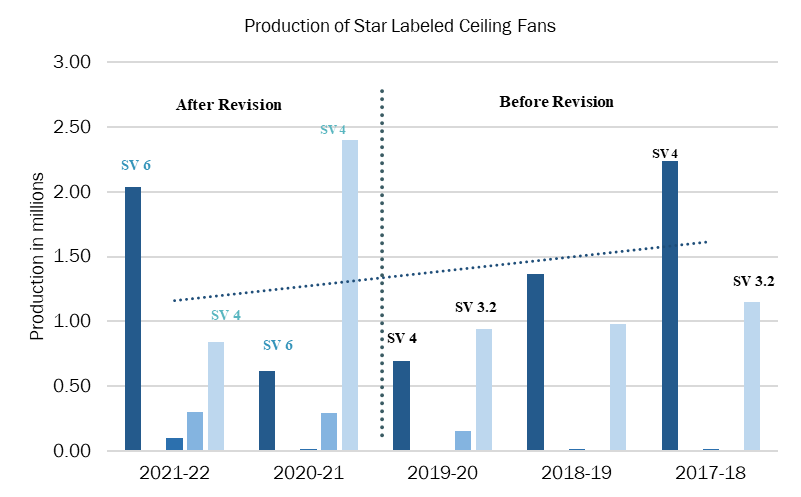
Source: GreenTree Analysis
Growth Trajectory of Super Efficient Ceiling Fans
The existing alignment of manufacturers has set a maximum service value of 9 for Energy-Efficient (EE) fans in the market. However, despite this alignment, low adoption rates persist due to high initial costs and the absence of a necessary regulatory framework to promote high-energy efficiency fans. Forecasts suggest that gradual revisions in benchmark service levels within the BEE Star Labelling program will aid in reducing prices through economies of scale, driving greater adoption of these appliances. As seen in the LED market under UJALA, a projected decline in prices is anticipated to boost volume and facilitate wider acceptance of these advanced, energy-efficient fans.
Our next article in the series will explore how the component’s efficiency may impact the appliance level efficiency. Please connect [email protected] if you have any query.
Stay tuned for the next article in series as we cover the topic in depth.


